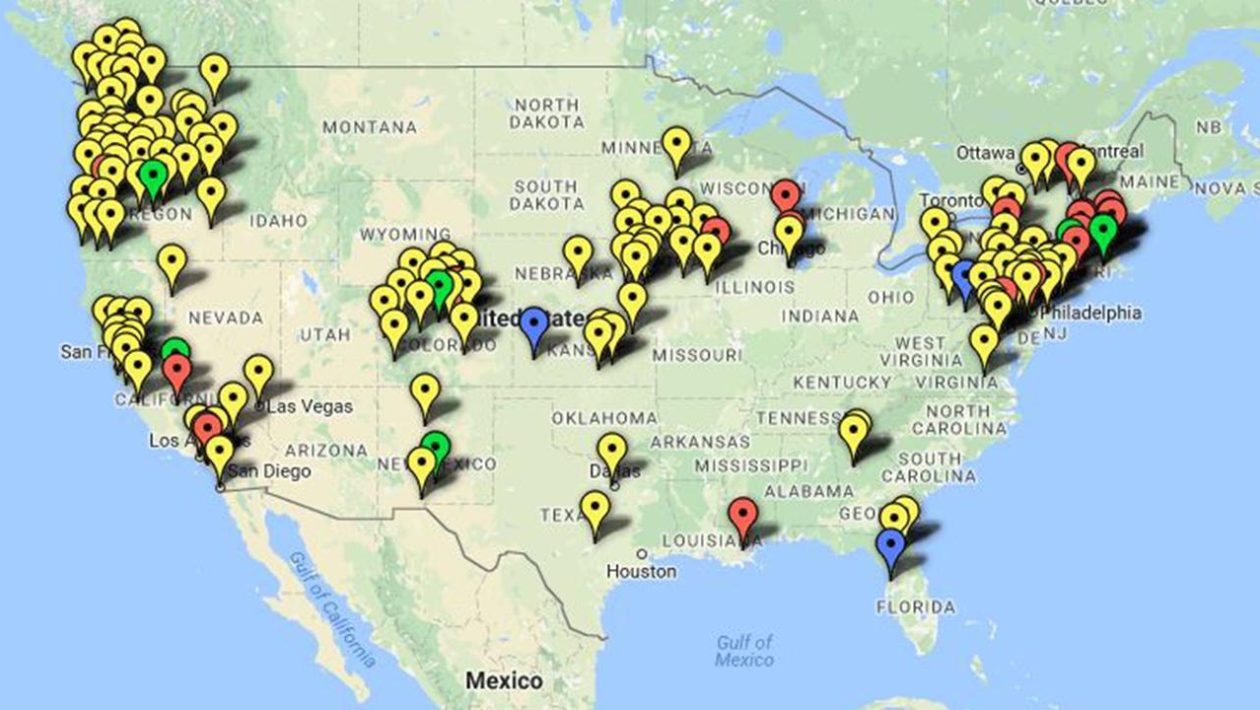
In response to closed borders, detention, and deportation efforts, communities nationwide declare themselves as sanctuary cities. These sanctuary cities can be found across the country, advocating for human rights principles, the division between local and federal law, and the empowerment of communities through immigrant contributions. The cities adopting sanctuary city policies do so for diverse reasons, all interconnected in some way with the principles of human rights and the development of their communities.
What are Sanctuary Cities?
The term “sanctuary city” often appears in the news, referring to municipalities that limit cooperation with federal immigration enforcement. Originating in the 1980s when the federal government denied asylum to Central American refugees, the movement has led to many cities, counties, and states passing ordinances to protect immigrants and refugees, offering information, documentation, and support for their integration. Local governments also provide resources like websites and apps for healthcare, education, and legal assistance.
Why sanctuary cities are essential and how the system works
Sanctuary cities today are places where local law enforcement avoids ICE duties without a warrant or local court order. Their policies often involve supporting faith-based organizations and movements. In the 1980s and 1990s, sanctuary began to be seen more as a human rights issue than purely religious. This led to a shift in focus towards policies reducing local police involvement in federal immigration matters.
Every city sets forth its own set of laws and regulations, leading to variations in the specific operational details within each city. A common thread among sanctuary cities is their restriction of resources available to federal immigration officers when attempting to apprehend undocumented immigrants. The subsequent passage illustrates a sequence of events and how sanctuary policies are applicable in such cases.
- Law enforcement detains an individual:
In the local or county jail, officers record the individual’s information and fingerprints, which are processed through the FBI database per procedure. Compliance with ICE regulations requires sharing inmate information among state and federal agents.
- ICE gets involved:
When ICE records indicate that the individual lacks documentation, a request is sent by ICE to the local jail, asking them to detain the individual for an extra 48 hours beyond the initially scheduled release day and time. This extended period enables ICE to pursue a warrant and initiate the deportation procedure.
Pros of sanctuary cities
These cities promote improved relationships between undocumented immigrants and law enforcement agencies. These sanctuary policies are considered legal and safeguarded by the U.S. Constitution’s Tenth Amendment. They serve as protective measures for undocumented immigrants against federal immigration laws.
Conclusion
Immigration issues are a source of concern for communities throughout the nation. Embracing immigrants and offering them resources and assistance, from a perspective of human rights, can achieve much more outstanding results than detaining and expelling them ever could. With the United States continuously expanding in its population and guiding principles, it is imperative to examine immigration from a humanitarian perspective rather than as a mere financial burden on the penal system. Sanctuary cities and communities persist in setting the precedent, leading by example in this regard.